A temperature sensor is a device used to measure temperature. It can be air temperature, liquid temperature, or solid object temperature. There are different types of temperature sensors available, each using different techniques and principles to measure temperature.
Definition of Temperature Sensor
The measurement of thermal energy in an object is temperature, and temperature is a major concern in most industries. The basic characteristic of temperature is that an increase or decrease in temperature affects the amount of kinetic energy of the particles in the component. A bowl of hot water has a lot of energy compared to a bowl of cold water.
We can define temperature as a measure of the kinetic energy of a molecule in a system. Temperature measurement is very important in an industrial process because variations in temperature levels can cause changes in physical or chemical conditions. Therefore, temperature measurement is very important to protect devices. If the temperature is not controlled, it will damage pipes and tanks.
How important is temperature measurement?
- Temperature affects the reaction rate.
- It affects viscosity.
- An increase or decrease in temperature can change the state of matter.
- The strength of the material has an effect.
- The security of the process depends on it.
- By adjusting the temperature, the efficiency, and quality of the product can be improved.
Types of Temperature Sensors
We can also classify temperature sensors into electrical and
Non-electrical Methods.
- Non-electrical methods – In this method, the sensor measures the temperature based on the change in volume of the liquid caused by the temperature.
- Temperature measurement can also be done based on the change in gas pressure caused by temperature fluctuations.
- Measurements are also made with changes in vapor pressure during temperature fluctuations.
Electronic Methods
- Thermocouples
- Measurements are also made with changes in material resistance due to temperature changes.
- Measurements are also made by determining the energy obtained by radiation.
Mechanical method (Non-electrical)
Bimetallic Thermometer
Thermometers are the oldest and most widely used temperature sensors for measuring temperature. This type of thermometer uses a bimetallic strip, which is made by welding two metal strips with different coefficients of thermal expansion.
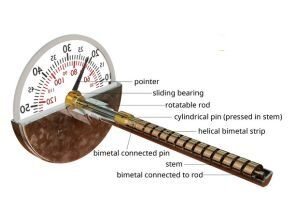
Thus, when this strip is exposed to heat, the metal changes its length according to its thermal expansion properties. Therefore, when heat is applied to it, a metal with a higher thermal coefficient expands faster than a metal with a lower thermal coefficient. Therefore, the entire metal strip bends towards the metal with a lower thermal coefficient.
Advantages of Bimetallic Thermometers
- Easy to maintain.
- Inexpensive.
- No power supply is required.
- Good temperature range.
Disadvantages of bimetallic thermometers
- Local installation.
- Calibration may change due to rough handling.
- Most pointers are available.
- Low accuracy.
- Limited applications.
What are the Applications of Bimetallic Thermometers
- It is used for the automatic control of home appliances.
- Machine temperature measurement.
- Reaction chamber.
- Furnaces.
- Adjust the air temperature.
- Process parameters can also be measured.
- Termostat?altilo.
- Mura thermometer.
Gas Thermometer
In this type of thermometer, the temperature is measured by determining the expansion of gas. Liquids and solids expand irregularly, but unlike gases, a gas expands uniformly as the temperature increases.

So, due to this property of gas, it is used to measure temperature. In this sensor, the gas is encapsulated in a thermostatic agent. When this sensor is exposed to heat, the pressure changes. The working principle of the gas thermometer conforms to Charles’ law, which states that as the temperature of the gas increases, the volume of the gas also increases. When the sensor is heated, the gas molecules gain more energy and move faster, thus increasing the sound volume.
Therefore, when the sensor is not exposed to temperature, the gas molecules have little energy and these molecules pack together and thus the volume is smaller. The most common gases used in these thermometers are nitrogen and helium. Nitrogen is cheaper and does not react with steel lamp material at high temperature. Nitrogen does not react well at low temperatures and we can use helium for that.
Advantages of Gas Thermometers
- Very accurate.
- Wide variety.
- Very sensitive.
- It does not depend on the type of gas used.
- The temperature response is fast compared to the type of liquid.
Disadvantages of Gas Thermometers
- Not easy to handle.
- Very sensitive to temperature changes and also mechanical vibration.
- Taking measurements takes a long time.
- Expensive
- Cannot be used to measure rapid temperature changes.
- Not portable.
Applications of Gas Thermometers
- Due to their high accuracy, they can also be used to calibrate other thermometers.
- Used to measure temperature in pipelines and tanks.
Electrical Method
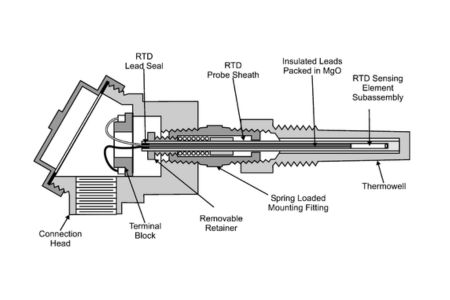
RTD
RTDs are temperature sensors and their principle of operation is based on the fact that the resistance of a metal increases as the temperature increases. That is why it is called a resistance temperature detector, the most commonly used metals for temperature measurement are nickel and platinum. These temperature sensors are available in different formats.
 RTD
RTD
RTDs are basically thin coils of platinum, most RTDs are made in two ways, using wire or film. The RTD output is electrical and therefore RTDs can be used whenever feedback is needed and corrective action can be taken in automated systems.
Types of TTK Wire
wound RTDs can be classified into two types, one consists of a coil of wire encased in glass and this is the type of RTD we see in most industrial applications. Another type of RTD wire is wrapped around a ceramic or glass core and then covered with chrome glass. So in this case the sensor wire is connected to the larger wire by soldering.
Thin film RTD
This type of RTD is made by depositing a thin layer of platinum on a ceramic substrate and then stabilizing it. The platinum is deposited in a resist pattern, usually with the resistance controlled by breaking the circuit in the trim region. After that, the guide wires are attached. This RTD is covered with a layer of glass for mechanical and moisture protection.
Coil element RTD
This type of RTD is made using a spiral coil of platinum sensing wire, this wire is inserted into the opening of the insulating spindle, thus providing a sentencing sensing element.
Hollow ring RTD
This type of RTD uses an exposed metal coil shaft, which increases contact with the liquid and reduces thermal mass, thus providing a faster response. This type of RTD is fully enclosed but is more expensive compared to other types of RTD operations.
What are the Benefits of TTK?
- Very accurate.
- Stable.
- Line resistance change.
- Good operating temperature range.
- It works well at high temperatures.
- The reaction is faster than thermocouples.
- Good interchangeability.
- Absolute temperature can be measured.
- Can measure from very low to high temperatures.
- RTD output is electrical, so it can be used with PLCs.
What are the disadvantages of TTK
- Power supply required.
- Expensive
- Shock and vibration can affect the measurement.
- It heats up by itself.
TTK Applications
- Textile production.
- Plastic processing.
- Microelectronics.
- petrochemicals.
- Can be used to measure the temperature of air, gases, and liquids.
- Ovens and grills.
- Can be used to measure flue gas temperature.
- Medical and chemical laboratories.
Thermistor
A thermistor can be described as a resistive material consisting of metal oxides and covered with glass. Thermistors are made of semiconductors, a mixture of certain oxides such as nickel, manganese, copper, cobalt, and other materials, and these materials are sintered at very high temperatures. In this type of temperature sensor, the resistance decreases as the temperature increases.

- Thermistor
Thermistors are made of semiconductor materials, the semiconductors used differ from the properties of the thermistor, such as sensitivity, temperature, resistance, etc. Thermistors can be classified into two types. One has a negative and the other a positive temperature coefficient. PTC thermistors have only a limited range and therefore NTC thermistors are more widely used.
The thermistor has good sensitivity, it shows a large change in resistance with a small change in temperature. Thus, thermistors are very sensitive. The main difference between thermistors and RTDs is the material used to construct them. The material used in thermistors can be either ceramic or polymer, while RTDs use pure metal. The sensitivity of thermistors is very high compared to RTD.
What are the Advantages of a Thermistor
- Inexpensive.
- Small size.
- Hypersensitivity.
- Point detection, this sensor can be converted into a small size needle for point detection.
- They are compatible with many devices.
What are the Disadvantages of a Thermistor
- Non-linear output.
- Limited temperature range.
- Delicate.
- Self-heating.
What are the Applications of Thermistors
- They can be used to turn off the temperature because it is very sensitive.
- Can be used to monitor battery temperature.
- Temperature monitoring of the incubator.
- PTC thermistors can be used as current limiting devices for circuit protection.
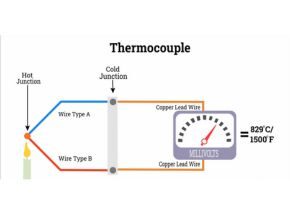
Thermocouple
Thermocouples are made by joining the ends of two different materials. Metals are joined by soldering or welding, the working principle of this device is the Seebeck effect. It states that when two dissimilar metals are joined together, and when the two junctions are at different temperatures, there is a current in the closed circuit between the two dissimilar materials.

- Thermocouple
Thus, when heat is applied to these devices, a voltage is generated, the voltage generated depends on the metals used and also the temperature between the junctions. Thermocouples are able to convert heat energy into electrical energy. If the temperature in both connections is the same, the voltages in both connections cancel each other and no current flows.
So when each junction has a different temperature, a different voltage is created and there is also a current in the circuit. So, to measure temperature with a thermocouple, one end of the thermocouple must be kept in contact with the process, and the other end at a constant temperature. The reference connection is the part of the sensor that has a constant temperature at the tip, and the part of the sensor that is in contact with the process is the measurement connection.
What are the Advantages of Thermocouples?
- It is widely used in many industries
- The structure is simple
- Solid
- Use at high temperatures
- Inexpensive
- Quick response to temperature changes
- Remote temperature measurement
- Can be used for various temperatures
- Calibration checks can be easily performed
- Long transmission distances can be achieved
What are the Disadvantages of Thermocouples
- Non-linear response
- Unstable
- Low repeatability
- Less sensitivity to small temperature changes
- Low accuracy
- The extension cord used must be the same type as the thermocouple
- The cable must be shielded, otherwise, it may receive radiated electrical noise
- It requires an amplifier for many applications
- Most control applications require expensive accessories.
What are the Applications of Thermocouples
- Medical devices
- Industrial heat treatment
- Packaging equipment
- Semiconductor processing
- Food Equipment
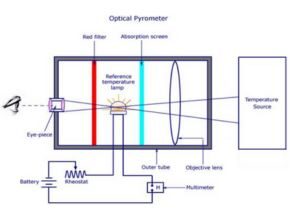
Optical pyrometer
This pyrometer has a bulb, a lens directs the radiation from the object to the bulb. In the picture, there is a red filter between the eyepiece and the lamp, which is arranged so that only a narrow band of wavelengths can pass through. The eyepiece is adjusted until the lamp is focused. By changing the value of the rheostat, the lamp heats up due to the current passing through it.

- Optical pyrometer
As the current increases, the temperature and resistance of the lamp increases. If the radiation intensity of the lamp is equal to the radiation intensity of the object or temperature source, the filament cannot be separated. So a multimeter connected to the lamp measures the current through it and we can use it to determine the temperature of the filament and therefore the target temperature.
What are the Advantages of a Pyrometer?
- No contact with the product
- Very fast response time
- No corrosion or oxidation affects measurement accuracy
- Stability – High repeatability
- Measurement of moving objects
- We can measure certain hard-to-reach objects What are the disadvantages of pyrometers
- High initial costs
- Very difficult due to electronic support required for measurement
- The background of dust or smoke affects the accuracy of the measurement
- Radiation
- The use of the sensor is limited by the field of view and also by the size of the point
- Cannot be used to obtain continuous temperature values
What are the Applications of Pyrometers
- It is used in automation and feedback control
- These sensors are used in manufacturing processes such as glass, metal, cement, semiconductor, etc.
- This sensor is useful for extinguishing fire
Conclusion
The following conclusions can be drawn from the article described above, namely “Definition and Types of Temperature Sensors”:
- A temperature sensor is a device that measures temperature. It can be air temperature, liquid temperature or solid object temperature. There are different types of temperature sensors available and each uses different techniques and principles to measure temperature.
- There are 3 types of temperature sensors, namely: mechanical method (non-electrical), electrical method and radiation method.
- Types of temperature sensors for mechanical processes: bimetallic thermometer and gas thermometer
- Types of temperature sensors with electrical method: RTD, thermistor, and thermocouple
- Types of temperature sensors radiation method: radiation pyrometer and optical pyrometer.
Refference : https://instrumentationtools.com/


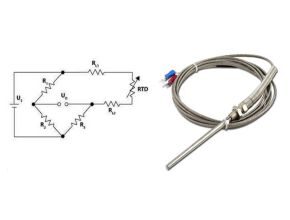 RTD
RTD